|
Parent Topic |
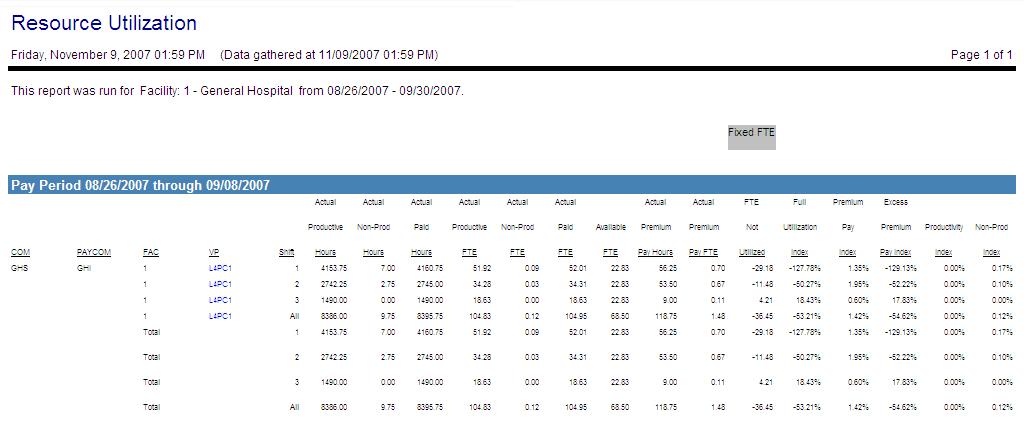
This report gives an overview of how FTE resources are used. This report is used to analyze what resources are used and displays a breakdown of how the hours are paid. This report helps determine whether or not changes could be made to scheduling in order to better utilize available resources.
Report fields include,  Actual Productive Hours,
Actual Productive Hours,  Actual Non-Prod Hours,
Actual Non-Prod Hours,  Actual Paid Hours,
Actual Paid Hours,  Actual Productive FTE,
Actual Productive FTE,  Actual Non-Prod FTE,
Actual Non-Prod FTE,  Actual Paid FTE,
Actual Paid FTE,  Available FTE,
Available FTE,  Actual Premium Pay Hours,
Actual Premium Pay Hours,  Actual Premium Pay FTE,
Actual Premium Pay FTE,  FTE Not Utilized,
FTE Not Utilized,  Full Utilization Index,
Full Utilization Index,  Premium Pay Index,
Premium Pay Index,  Excess Premium Pay Index,
Excess Premium Pay Index,  Productivity Index,
Productivity Index,  Non-Prod Index.
Non-Prod Index.
The percentage of FTEs that were assigned non-productive hours during the reporting period, such as vacation or sick time.
Formula: ( Non-Productive FTE /
Non-Productive FTE /  Productive FTE) * 100
Productive FTE) * 100
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
The number of FTEs working non-productive hours.
Formula:  Non-Productive Hours /
Non-Productive Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
Formula: ((Target FTE - Productive FTE) / Target FTE) * 100
Shows the percentage of staff who were paid premium pay (such as overtime) that could have been prevented by assigning shifts to underutilized staff.
Formula:  Full Utilization Index -
Full Utilization Index -  Premium Pay Index
Premium Pay Index
Determines the percentage of staff who were paid premium (higher cost) pay.
Formula: ( Premium FTE /
Premium FTE /  Productive FTE) * 100
Productive FTE) * 100
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
The FTEs receiving premium (higher cost) pay.
Formula:  Premium Hours /
Premium Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Premium Pay is set to Yes. These are shifts that are awarded premium (higher cost) pay.
This value determines how much of the available staff was used. Ideal utilization is 100%. Less than 100% means all available staff wasn't used; more than 100% means staff was over used.
Formula: ((Available FTE - Paid FTE) / Available FTE) * 100
Determines the percentage of staff who were paid premium (higher cost) pay.
Formula: ( Premium FTE /
Premium FTE /  Productive FTE) * 100
Productive FTE) * 100
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
The FTEs receiving premium (higher cost) pay.
Formula:  Premium Hours /
Premium Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Premium Pay is set to Yes. These are shifts that are awarded premium (higher cost) pay.
This value determines how much of the available staff was used. Ideal utilization is 100%. Less than 100% means all available staff wasn't used; more than 100% means staff was over used.
Formula: ((Available FTE - Paid FTE) / Available FTE) * 100
The FTEs that were available for working but did not work.
Formula:  Available FTE -
Available FTE -  Paid FTE
Paid FTE
The sum of the paid hours for the FTEs, including the productive and non-productive hours.
Formula:  Productive FTE +
Productive FTE +  Non-Productive FTE
Non-Productive FTE
The number of FTEs working non-productive hours.
Formula:  Non-Productive Hours /
Non-Productive Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
The number of  FTE's configured for the productivity standard or job class/position.
FTE's configured for the productivity standard or job class/position.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
The FTEs receiving premium (higher cost) pay.
Formula:  Premium Hours /
Premium Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Premium Pay is set to Yes. These are shifts that are awarded premium (higher cost) pay.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Premium Pay is set to Yes. These are shifts that are awarded premium (higher cost) pay.
The number of  FTE's configured for the productivity standard or job class/position.
FTE's configured for the productivity standard or job class/position.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
The sum of the paid hours for the FTEs, including the productive and non-productive hours.
Formula:  Productive FTE +
Productive FTE +  Non-Productive FTE
Non-Productive FTE
The number of FTEs working non-productive hours.
Formula:  Non-Productive Hours /
Non-Productive Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
The number of FTEs working non-productive hours.
Formula:  Non-Productive Hours /
Non-Productive Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
The sum of the direct and indirect productive FTE values. This indicates the number of FTEs who actually worked.
Formula:  Productive Direct FTE +
Productive Direct FTE +  Productive Indirect FTE
Productive Indirect FTE
The number of FTEs working hours assigned to pay codes that are coded to be productive and indirect.
Formula:  Productive Indirect Hours /
Productive Indirect Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours /
Productive Direct Hours /  FTE Hours Conversion
FTE Hours Conversion
 FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
FTE hours / number of productive days in week) * number of productive days in reporting period.
Acronym for "full time equivalent". This compares the number of hours worked by employees to the value set for a full time employee. If the value for an FTE is set to 40 hours per week, then every 40 hours worked would equal 1.0 FTE.
For example, if several employees worked a total of 300 hours, this would be 7.5 FTEs, regardless of how many individual employees worked these 300 hours (300 / 40 = 7.5).
The number of hours which define the productivity FTE for the corporation are set up on the Configuration section > System card > Application screen. Enter "LBRVSN" in the Code field and Search. Open the Parameters tab.
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
Sum of hours employees are paid for, including hours actually worked and paid time off (such as vacation).
Formula:  Productive Hours +
Productive Hours +  Non-Productive Hours
Non-Productive Hours
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
Total of both the direct and indirect productive hours.
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours +
Productive Direct Hours +  Productive Indirect Hours
Productive Indirect Hours
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Non-Productive Hours (Paid) is set to Yes. Non-productive hours are usually associated with paid time off, such as sick time, vacation, jury duty, etc.
Total of both the direct and indirect productive hours.
Formula:  Productive Direct Hours +
Productive Direct Hours +  Productive Indirect Hours
Productive Indirect Hours
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Indirect Hours (Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes. These are shifts where the employee is not directly providing patient care (for example, maintenance, laundry, or education classes).
Total of the hours assigned to pay codes where report assignment Productive Direct Hours (Direct, Worked, and Paid) is set to Yes and where neither the job class nor any special codes are set to be Indirect. These are shifts where the employee is directly providing patient care (for example, RN or LPN).
The hours are considered to be direct when ALL of the following are true:
This report includes Labor Distribution Drill down/roll up with in the report.
Click on the name of a labor distribution to expand to the next lower level and show details. The lowest level displayed is either the job class or the productivity standard.
If the report is run at a lower distribution level, the totals displayed when rolling up only include those from the selected organization unit. For example, if the report is run for Department A at level 5, if you open the level 1 Corporate labor distribution, the values included are only those from Department A, not from the entire corporation. However, if the report is run for the Corporate level 1, the user can drill down to level 5 and view the amounts for Department A.
Report parameters include the following options: